The transition to renewable energy is accelerating, but this growth brings challenges, particularly around congestion, curtailment, and market risks. With EDF Renewables North America (EDF RNA), we, at the EDF Innovation Lab, are exploring innovative ways to optimize renewable energy assets by pairing them with flexible load technologies. These technologies not only address operational challenges but also unlock new revenue streams and support the decarbonization of various industries.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of the opportunities, challenges, and emerging solutions that are currently at the forefront of our efforts. This highlights how EDF Group is leveraging Open Innovation to drive business growth, and how the Innovation Lab is collaborating closely with Business Units to swiftly address key challenges.
Why New Load is Key for Renewable Optimization
Operating renewable assets comes with financial risks, particularly in regions like Texas, where congestion between generation and consumption hubs is common. These risks manifest in two main ways:
- Basis Risk: When the price at the generation node is lower than the price at the settlement hub.
- Curtailment: When excessive generation leads to negative prices, forcing assets to stop producing.
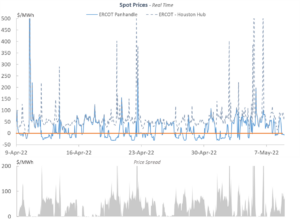
Pairing renewable energy with co-located, flexible load can mitigate these risks. Such arrangements allow assets to:
- Increase revenue during curtailment periods.
- Provide below market cost energy.
- Offer fixed prices to mitigate market exposure for both producers and consumers, or indexed nodal pricing that provides benefits to consumers typically paying retail rates.
Three Use Cases for Co-Located Flexible Load
Existing renewable assets often have hedges in place, which can take various forms depending on the Independent Power Producer’s (IPP) initial negotiations during project financing. Defined-quantity hedges retain volume risk, while as-generated PPAs are exposed to basis risk. Additionally, assets may transition to merchant status after the initial hedge expires. Each of these scenarios presents unique benefits for a new co-located offtaker.
- Assets with existing Defined Quantity Hedges: Off-takers can access electricity at nodal prices, plus a small adder, while otherwise he would pay a higher retail price.
- Assets with PPAs: BTM installations ensure electricity is not curtailed by the grid operator. Off-takers can access very low electricity price that otherwise would be curtailed.
- Merchant Assets: Co-located load can provide a guaranteed fixed price, removing market price exposure. Off-takers benefit from lower costs since risk premiums in case of bases risks are not included.
Innovative Technologies for Co-Located Flexible Load
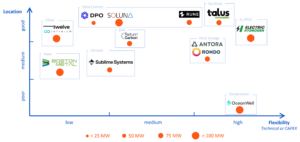
Our innovation journey has led us to explore several technologies with varying levels of maturity (TRL) and operational needs, including but not limited to:
- Hydrogen and E-Fuels:
- Opportunity: Hydrogen production benefits from tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), while e-fuels combine hydrogen and captured CO2 for decarbonization.
- Challenge: Often high CAPEX and location-specific requirements, and sometime not able to follow the intermittency of renewables, and IRS guidance on additionality for tax credits may pose barriers.
- Notable Player: Electric Hydrogen’s low-CAPEX electrolyzers are promising for 100 MW-scale projects.
- Thermal Energy Storage:
- Opportunity: Converts renewable electricity into stored heat, which can be used by nearby industries.
- Challenge: Requires off-takers located within 6 miles of renewable sites.
- Notable Player: Rondo Energy, which has already piloted successful projects in California.
- Data Centers:
- Opportunity: Emerging use cases, such as crypto mining and AI training, show potential for leveraging renewable power.
- Challenge: Limited flexibility in operations.
- Notable Player: Rune, a developer of low-CAPEX, flexible data centers.
- Industrial Processes (Steel, Cement):
- Opportunity: Green steel and cement production can drastically reduce carbon emissions.
- Challenge: High CAPEX and often inflexible operations.
- Notable Player: Sublime Systems, working on low-carbon cement with pilot projects underway.
- Fertilizer Production:
- Opportunity: Ammonia-based fertilizers can operate with low capacity factors, aligning with renewable availability.
- Challenge: IRS guidance on additionality for tax credits may pose barriers.
- Notable Player: Talus Renewables, which has modular solutions for quick deployment.
In addition, technologies such as Direct Air Capture, Long Duration Energy Storage, and even water desalination may also be worth exploring, though they often face implementation challenges.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities
While the potential for innovative flexible load technologies is clear, several challenges remain:
- Flexibility: Many technologies need to adapt to renewable intermittency.
- Location Constraints: Some processes require specific resources (e.g., water, feedstock) that may not align with renewable asset locations. Furthermore, some off-takers are looking for specific areas where their end product can easily be used or transport.
- Economic Viability: High CAPEX technologies often require significant annual uptime which is not compatible with using only underutilized renewable generation.
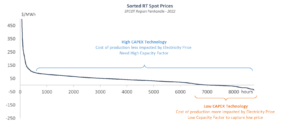
Despite these hurdles, there is growing interest from startups and established players. Our mission at the Innovation Lab was to identify some compatible companies.
In early 2025, EDF Renewables North America released an RFP with the aim of engaging with partners to explore scalable solutions.
Conclusion: Pioneering a New Era of Renewable Asset Optimization
The integration of innovative flexible load technologies marks a significant step forward in renewable energy optimization. By aligning renewable generation with flexible, co-located demand, we can mitigate market risks, enhance profitability, and contribute to the decarbonization of traditionally carbon-intensive industries.
This collaboration with EDF Renewables North America highlights how corporate innovation can drive significant impact within a global organization like EDF. Our vision of success includes EDF Renewables partnering with innovative companies to secure behind-the-meter (BTM) PPAs, enabling the delivery of affordable, carbon-free electricity. This approach not only supports electrification but also makes a tangible contribution to combating climate change.
If this topic resonates with you or if you have ideas about technologies that align with these needs, we’d love to hear from you. Feel free to reach out to us or to EDF Renewables North America and join the conversation! Gabe Massercola, Capital Improvements Associate Director, is leading this effort for EDF Renewables North America.
Olivier Deneux, Innovation Director


